
SOLUTIONS
What is Being Done to
Solve Climate Change?
Taking the right steps to mitigate and
address the impacts of climate change is crucial.
Addressing climate change requires collective efforts from the entire society, governments, businesses, and organizations worldwide.
Here are some solutions and actions that can be taken to reduce the impacts of climate change:
1. Shifting to Clean Energy
 Photo: climate.nasa.gov
Photo: climate.nasa.govClean energy refers to energy sources and technologies that have lower environmental impacts or even do not pollute the environment compared to conventional energy sources widely used. Clean energy focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and other negative impacts on the environment.
Renewable Energy includes:
Solar Energy:
Solar power plants use sunlight to generate electricity.Solar power plants use sunlight to generate electricity.Wind Energy:
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity.Hydro Energy:
Hydropower plants convert the energy of flowing water into electricity.Biomass Energy:
Biomass, such as organic waste and wood, is used to generate thermal energy or electricity. Biomass, such as organic waste and wood, is used to generate thermal energy or electricity.Geothermal Energy:
Heat from the Earth is used to produce steam that drives electric turbines.
Nuclear Energy:
Nuclear Reactors:
Despite controversy, nuclear power plants use nuclear reactions to generate energy without producing greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
Passive Energy and Energy Efficiency:
Energy-Efficient Building Design:
Buildings designed to minimize energy consumption and maximize the use of natural resources.Energy-Efficient Household Appliances:
Electronic and household appliances designed to reduce energy consumption.
However, it is important to note that some clean energy technologies also have challenges and environmental impacts that need to be managed, such as the environmental impact of the production and disposal of specific renewable technology materials. Therefore, clean energy sources must be developed and implemented considering sustainable and environmental aspects.
2. Reforestation and Forest Conservation
 Source: Pexels
Source: PexelsReforestation and forest conservation play crucial roles in mitigating climate change, preserving biodiversity, and ensuring the overall health of ecosystems. Here are key aspects and strategies related to reforestation and forest conservation:
Reforestation:
Tree Planting Programs:
Initiate large-scale tree planting programs to restore deforested or degraded areas. Prioritize native tree species that are well-suited to the local ecosystem.Agroforestry:
Promote agroforestry practices, integrating trees into agricultural landscapes for sustainable land use. Combining crops with trees helps improve soil fertility, retain water, and sequester carbon.Community Engagement:
Involve local communities in reforestation efforts, considering their knowledge of the land and fostering a sense of ownership. Provide incentives for communities to protect and care for newly planted trees.Urban Reforestation:
Implement tree planting initiatives in urban areas to enhance air quality, provide shade, and reduce the urban heat island effect.Technology and Monitoring:
Use technology, such as satellite imagery and drones, to monitor reforestation efforts and assess the health of newly planted trees. Implement data-driven approaches to optimize planting strategies.
Forest Conservation:
Protected Areas and Reserves:
Establish and enforce protected areas and reserves to safeguard critical ecosystems and prevent deforestation. Include buffer zones to minimize human impact around protected areas.Anti-Deforestation Policies:
Enact and enforce policies that penalize illegal logging and land conversion. Provide incentives for sustainable forestry practices, including certification programs.Forest Fire Prevention and Management:
Implement measures to prevent and manage forest fires, which can contribute significantly to deforestation. Use controlled burns and early detection systems to reduce the impact of wildfires.Corporate Responsibility:
Encourage responsible sourcing of forest products by promoting sustainable and certified wood products. Hold companies accountable for their supply chains and ensure they adhere to sustainable and ethical practices.Education and Awareness:
Raise awareness about the importance of forests and the role they play in climate regulation and biodiversity. Educate communities on sustainable forest management practices.Raise awareness about the importance of forests and the role they play in climate regulation and biodiversity. Educate communities on sustainable forest management practices.
3. Sustainable Agriculture
 The Importance of Sustainable Agriculture. (Plug & Play Tech)
The Importance of Sustainable Agriculture. (Plug & Play Tech)Promote sustainable agricultural practices that reduce emissions, conserve soil health, and enhance carbon sequestration. Encourage the use of agroecological methods and precision farming.
Sustainable agriculture aims to meet current food needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It involves practices that are environmentally sound, economically viable, and socially responsible. Here are key principles and strategies for sustainable agriculture:
Crop Diversity:
Promote the cultivation of a diverse range of crops to enhance resilience to pests, diseases, and environmental changes. Use crop rotation and diversification to improve soil health and fertility.Agroecology:
Adopt agroecological principles that mimic natural ecosystems, emphasizing biodiversity, soil health, and integrated pest management. Use companion planting and polyculture to create balanced, self-sustaining systems. Adopt agroecological principles that mimic natural ecosystems, emphasizing biodiversity, soil health, and integrated pest management. Use companion planting and polyculture to create balanced, self-sustaining systems.Soil Health Management:
Implement conservation tillage and no-till farming to reduce soil erosion and improve water retention. Apply organic matter, cover crops, and crop residues to enhance soil fertility and structure.Water Conservation:
Implement efficient irrigation practices, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, to minimize water use. Use technologies like soil moisture sensors to optimize water application.Organic Farming:
Embrace organic farming practices that avoid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, promoting natural pest control and nutrient cycling. Use compost and organic amendments to enhance soil fertility.Reduced Food Waste:
Minimize post-harvest losses through better storage, transportation, and processing techniques. Educate farmers and consumers about the impact of food waste on sustainability.Local and Direct Markets:
Support local and direct markets, such as farmers' markets and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs. Shorten supply chains to reduce the environmental impact of transportation.Education and Training:
Provide farmers with training and information on sustainable agricultural practices. Raise awareness among consumers about the importance of supporting sustainable agriculture.
4. Circular Economy
 Circular Economy. (European Commission)
Circular Economy. (European Commission)The circular economy is an economic model that seeks to minimize waste and make the most of resources by promoting sustainability, recycling, and reuse. In a circular economy, products, materials, and resources are kept in use for as long as possible, and at the end of their lifecycle, they are recovered, regenerated, and reintegrated into the production system. Here are key principles and strategies associated with the circular economy:
Design for Longevity:
Design products with durability and longevity in mind to extend their lifecycle. Consider modular designs that allow for easy repair, upgrade, and disassembly.Reuse and Refurbishment:
Promote the reuse of products and components to extend their life. Support refurbishment and remanufacturing practices to bring used products back to a like-new condition.Recycling:
Establish efficient recycling systems to recover valuable materials from products at the end of their life. Encourage the use of recycled materials in manufacturing processes.Waste Reduction:
Minimize waste generation by designing products with minimal packaging. Encourage businesses and consumers to reduce, refuse, and rethink consumption patterns.Resource Efficiency:
Optimize the use of resources in production processes to reduce waste. Implement resource-efficient technologies and practices to maximize the value derived from raw materials.Product as a Service (PaaS):
Explore business models where consumers pay for the service or function of a product rather than owning it outright. Manufacturers retain ownership and responsibility for product maintenance and recycling.Digital Technologies:
Leverage digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), to enable better tracking, monitoring, and management of resources throughout their lifecycle. Use data analytics to optimize resource use and product performance.Educational Initiatives:
Raise awareness among businesses and consumers about the principles and benefits of the circular economy. Educate people on how to participate in circular practices.
5. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
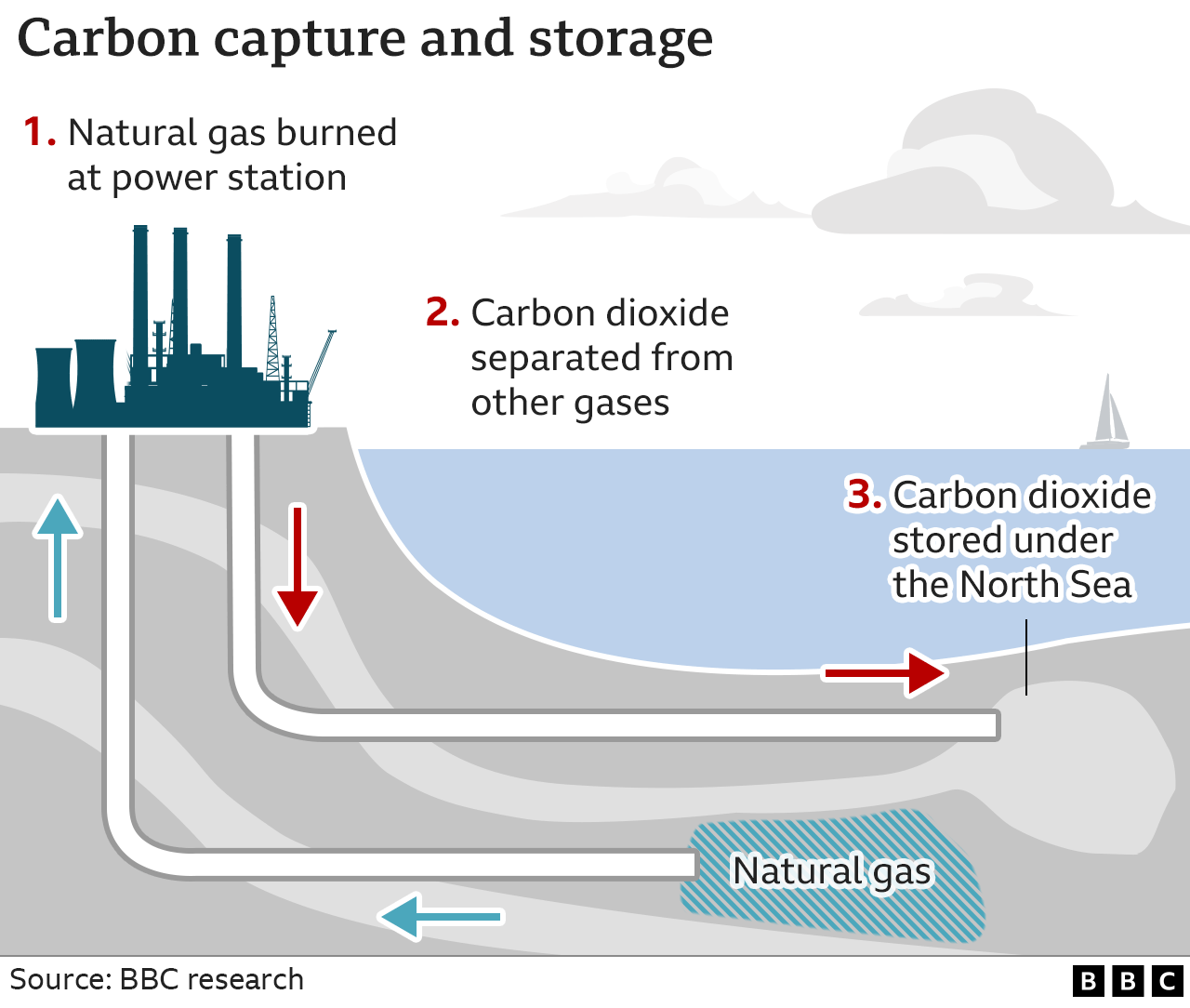
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) is a technology designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), from industrial processes and power generation. It involves capturing CO2 emissions at the source, transporting it to a storage site, and securely storing it underground to prevent its release into the atmosphere. Here are the key components and considerations associated with CCS:
Capture:
Post-Combustion Capture:
Captures CO2 emissions after fossil fuels are burned to generate electricity or industrial processes.Pre-Combustion Capture:
Separates CO2 before combustion during the conversion of fossil fuels into gas.Oxy-Fuel Combustion:
Burns fossil fuels in oxygen rather than air, resulting in a concentrated CO2 stream that is easier to capture.
Transport:
CO2 is transported from the capture site to the storage site using pipelines, ships, or trucks. Existing pipelines, if available, can be repurposed for transporting CO2.
Storage:
Geological Storage:
Injecting CO2 into geological formations such as depleted oil and gas fields, deep saline formations, or unminable coal seams.Ocean Storage:
Injecting CO2 into deep ocean sediments, a less common and more controversial method.
6. Public Transportation and Active Transportation

 Photo: ANTARA FOTO/Asprilla Dwi Adha/awwPhoto: Liputan6.com/Immanuel Antonius
Photo: ANTARA FOTO/Asprilla Dwi Adha/awwPhoto: Liputan6.com/Immanuel AntoniusPublic transportation and active transportation play crucial roles in addressing climate change by promoting sustainable and low-carbon mobility options. These modes of transportation contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, alleviating traffic congestion, and improving air quality. Here are the key aspects of how public and active transportation contribute to climate change solutions:
Reduced Emissions:
Public transit options, such as buses, trains, and subways, typically have lower per-passenger emissions compared to individual car travel, especially if they use cleaner energy sources.Efficient Land Use:
Public transportation encourages compact and efficient land use, reducing the need for sprawling urban development and limiting emissions associated with transportation.Equitable Access:
Public transportation provides affordable and accessible transportation options, promoting social equity and reducing dependence on individual car ownership.Improved Air Quality:
Active transportation reduces reliance on motor vehicles, leading to improved air quality and reduced pollution levels.Health Benefits:
Walking and cycling promote physical activity, contributing to public health by reducing the incidence of sedentary-related diseases.Community Connectivity:
Active transportation fosters community connectivity, encouraging social interaction and a sense of belonging.Reduced Noise Pollution:
Unlike motorized transportation, walking and cycling produce minimal noise pollution, contributing to a quieter and more pleasant urban environment.
7. Climate-friendly Urban Planning
 https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/sustainable-development-goals/why-do-sustainable-development-goals-matter/goal-11
https://www.unep.org/explore-topics/sustainable-development-goals/why-do-sustainable-development-goals-matter/goal-11Climate-friendly urban planning involves designing and developing cities in a way that mitigates and adapts to climate change. It focuses on creating sustainable, resilient, and environmentally friendly urban environments. Here are key principles and features of climate-friendly urban planning:
Compact and Mixed-Use Development:
Encourage compact urban development and mixed land-use zoning to reduce the need for long-distance travel, lowering energy consumption and emissions.Green Spaces and Urban Greening:
Integrate green spaces, parks, and urban forests to enhance biodiversity, provide recreational areas, and mitigate the urban heat island effect. Implement green roofs and walls to improve insulation and reduce energy consumption.Energy-Efficient Buildings:
Promote energy-efficient building design and construction standards to reduce the carbon footprint of urban infrastructure. Encourage the use of renewable energy sources for buildings, such as solar panels and wind turbines.Climate-Resilient Infrastructure:
Design infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and utilities, to withstand the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels. Implement green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and sustainable drainage systems, to manage water runoff.
8. Education and Advocacy
 7 Resource to Teach Students About Climate Change. (teachingchannel.com)
7 Resource to Teach Students About Climate Change. (teachingchannel.com)Education and advocacy are critical components of addressing climate change. They play a vital role in raising awareness, fostering understanding, and mobilizing individuals, communities, and policymakers to take meaningful action. Here are key aspects of education and advocacy about climate change:
Formal Education:
Integrate climate change education into school curricula at all levels to ensure that students develop a comprehensive understanding of the science, impacts, and solutions. Promote interdisciplinary approaches that connect climate change to subjects like science, geography, economics, and social studies.Higher Education and Research:
Support climate change research and academic programs at universities to advance scientific knowledge and provide a foundation for evidence-based policymaking. Encourage interdisciplinary research collaborations to address the complex challenges of climate change.Online Resources:
Create and disseminate online resources, such as webinars, courses, and informative websites, to reach a broader audience. Utilize digital platforms to share up-to-date information and resources.Professional Training:
Provide training programs for professionals in various sectors, including business, agriculture, and urban planning, to incorporate climate-friendly practices into their work.Public Awareness Campaigns:
Launch public awareness campaigns to inform the general population about climate change, its causes, and potential consequences. Use various media channels, including TV, radio, social media, and print, to reach diverse audiences.Community Workshops and Events:
Conduct community workshops and events to engage people at the local level. Offer practical information on sustainable living, energy efficiency, and climate resilience.Partnerships with Educational Institutions:
Collaborate with schools, colleges, and universities to facilitate guest lectures, workshops, and educational initiatives on climate change. Foster partnerships between educational institutions and environmental organizations.
9. International Cooperation
 Climate Action Summit 2019 (ilo.org)
Climate Action Summit 2019 (ilo.org)Collaborate globally to address climate change, share technology and knowledge, and establish binding agreements.
Support developing nations in adopting sustainable practices and adapting to climate impacts.
10. Innovation and Research
Invest in research and development to discover new technologies and strategies for mitigating and adapting to climate change.
11. Policy and Regulation
Implement and enforce policies that incentivize sustainable practices and penalize environmentally harmful activities.
Set emission reduction targets and regularly update regulations to reflect scientific advancements.
12. Individual Action
Encourage individuals to adopt sustainable lifestyles, reduce energy consumption, and make environmentally conscious choices.
Combating climate change requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, communities, and individuals. The combination of these solutions, along with ongoing innovation and adaptation, can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.